As the academic year comes to an end, students at the University of Salford conclude their journey with the challenging yet rewarding task of dissertation research. The 2023-2024 set from the MSc Data Science and MSc Artificial Intelligence programs has produced a diverse array of dissertation titles, reflecting dynamic interests and innovative approaches. To understand the prevailing themes and methodologies, I conducted a comprehensive analysis of these dissertation titles.

The analysis involved a thorough examination of the dissertation titles, focusing on word frequency, topic modeling, and common phrases. Common stopwords were filtered out, and sophisticated text analysis techniques such as Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) were applied to uncover the dominant themes and trends shaping the research landscape at the university.
TITLE LENGTH ANALYSIS
The descriptive statistics for the length of dissertation titles are:
Count: 116 titles
Mean: 90.25 characters
Standard Deviation: 32.93 characters
Minimum: 29 characters
25th Percentile: 63 characters
Median (50th Percentile): 88.5 characters
75th Percentile: 110.25 characters
Maximum: 198 characters
Most dissertation titles are around 90 characters long, with a wide range from 29 to 198 characters. This indicates a significant variation in title length.
AVERAGE WORD LENGTH AND TEXT COMPLEXITY
The descriptive statistics for the average word length and word count of dissertation titles are:
Average Word Length:
Mean: 6.58 characters
Standard Deviation: 0.82 characters
Minimum: 4.8 characters
25th Percentile: 6.10 characters
Median (50th Percentile): 6.5 characters
75th Percentile: 7.14 characters
Maximum: 9 characters
Mean: 12.14 words
Standard Deviation: 4.60 words
Minimum: 3 words
25th Percentile: 8 words
Median (50th Percentile): 11 words
75th Percentile: 15 words
Maximum: 26 words
Most titles have an average word length of around 6.58 characters and contain about 12 words on average, indicating moderate complexity in terms of word length and count.

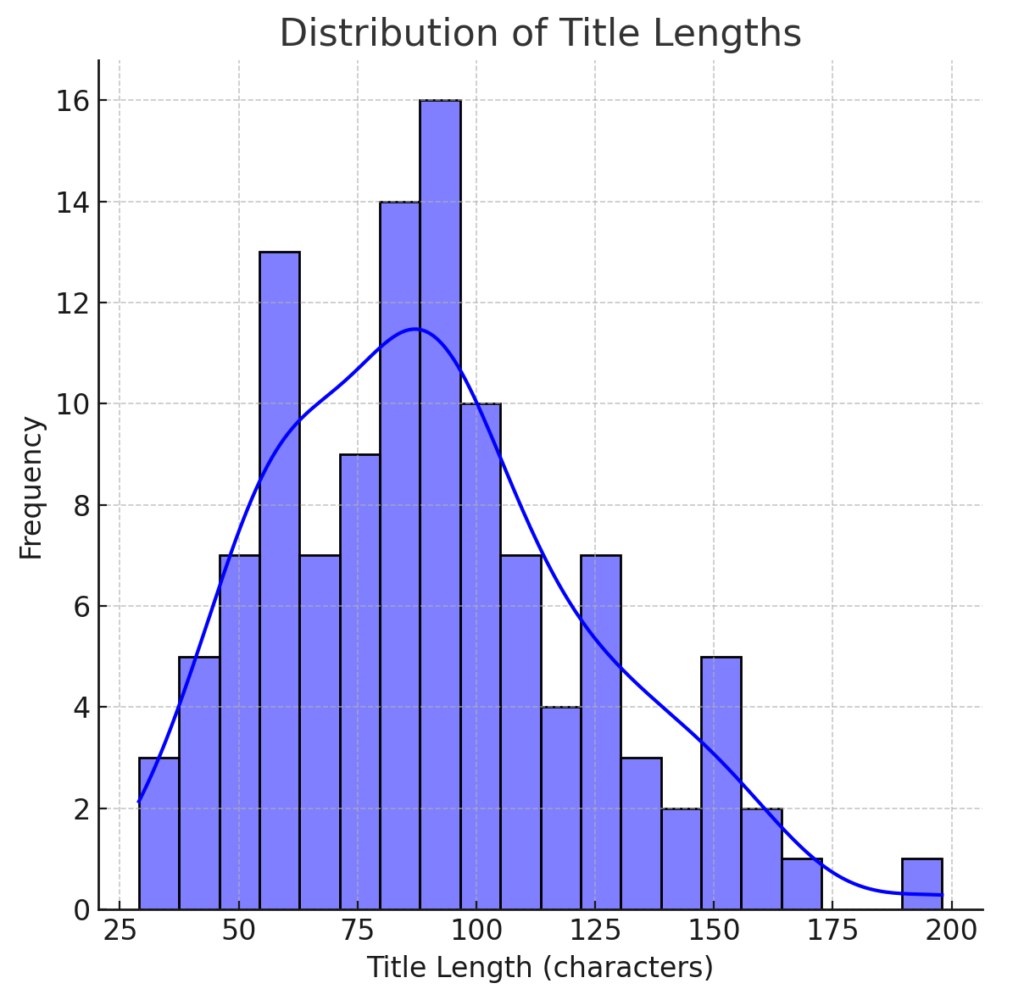
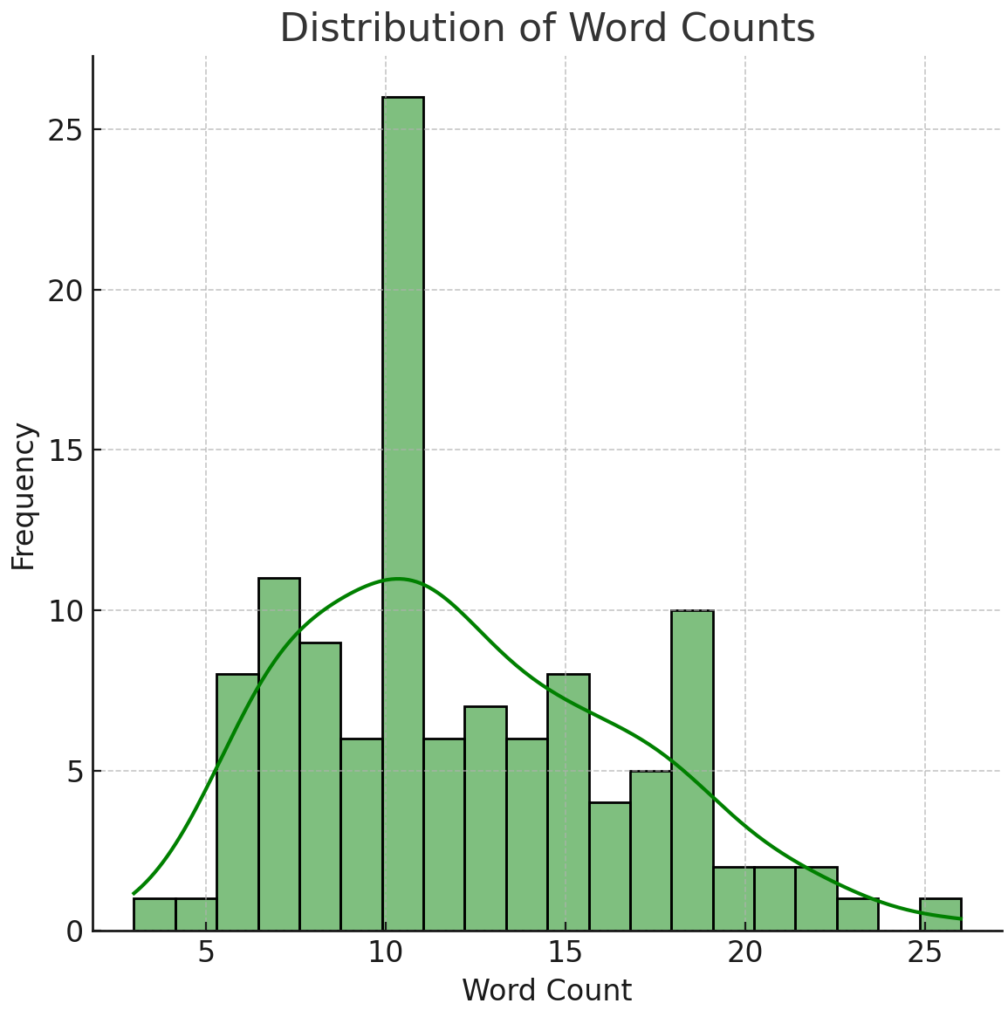
The majority of dissertation titles are between 50 and 150 characters long, with a peak around 80-100 characters.
There is a significant range in title lengths, indicating diversity in title structure and detail.
Most dissertation titles have between 8 and 15 words, with a peak around 10-12 words. This suggests that while there is some variability, most titles are concise yet descriptive.
The average word length in dissertation titles mostly falls between 6 and 7 characters.
This distribution shows that titles typically use moderately long words, contributing to their complexity and how informative they are.
WORD FREQUENCY AND N-GRAM ANALYSIS
The most common words in the dissertation titles, after filtering out stopwords, are:
learning (55 occurrences)
using (43 occurrences)
machine (33 occurrences)
detection (22 occurrences)
deep (21 occurrences)
analysis (18 occurrences)
predicting (16 occurrences)
approach (13 occurrences)
data (13 occurrences)
prediction (11 occurrences)
classification (10 occurrences)
predictive (9 occurrences)
customer (9 occurrences)
techniques (9 occurrences)
enhancing (9 occurrences)
models (8 occurrences)
model (8 occurrences)
child (7 occurrences)
ai (7 occurrences)
language (7 occurrences)
Common Bigrams:
machine learning (32 occurrences)
deep learning (18 occurrences)
using machine (12 occurrences)
learning approach (10 occurrences)
using deep (8 occurrences)
credit card (6 occurrences)
detection using (6 occurrences)
prediction using (5 occurrences)
time series (4 occurrences)
learning techniques (4 occurrences)
Common Trigrams:
using machine learning (12 occurrences)
using deep learning (8 occurrences)
machine learning approach (7 occurrences)
prediction using machine (4 occurrences)
machine learning techniques (3 occurrences)
detection using machine (3 occurrences)
natural language processing (3 occurrences)
machine learning methods (3 occurrences)
deep learning approach (3 occurrences)
deep learning models (2 occurrences)
Interpretation
From the word frequency analysis, the prevalent terms highlight the key areas of focus in the dissertation titles
Learning and Machine Learning: These terms dominate the titles, indicating a strong emphasis on machine learning techniques.
Using and Approach: These terms suggest that many dissertations focus on applying specific methods or approaches to problems.
Detection, Analysis, Prediction: These terms reflect common research activities such as analyzing data, making predictions, and detecting patterns or anomalies.
Deep (referring to deep learning): Shows a specific interest in advanced neural network techniques.
Data: Emphasizes the importance of data in the research topics.
Customer, Child, AI: Indicates specific application areas or technologies being researched.
The bigram and trigram analysis provides further insights into the common research themes and methodologies:
Machine Learning: Both bigrams and trigrams frequently mention “machine learning” and “deep learning,” indicating these are central techniques in the research.
Using: The frequent appearance of “using” in bigrams and trigrams suggests a focus on the application of these techniques.
Approach, Techniques, Methods: These terms in the context of “learning” highlight a focus on developing or applying different methods and techniques.
Specific Applications: Terms like “credit card,” “time series,” and “natural language processing” point to specific applications of machine learning and data analysis techniques.
These analyses complement each other, providing a comprehensive view of the main research areas and methodologies in the dissertation titles.
Word Cloud Visualization
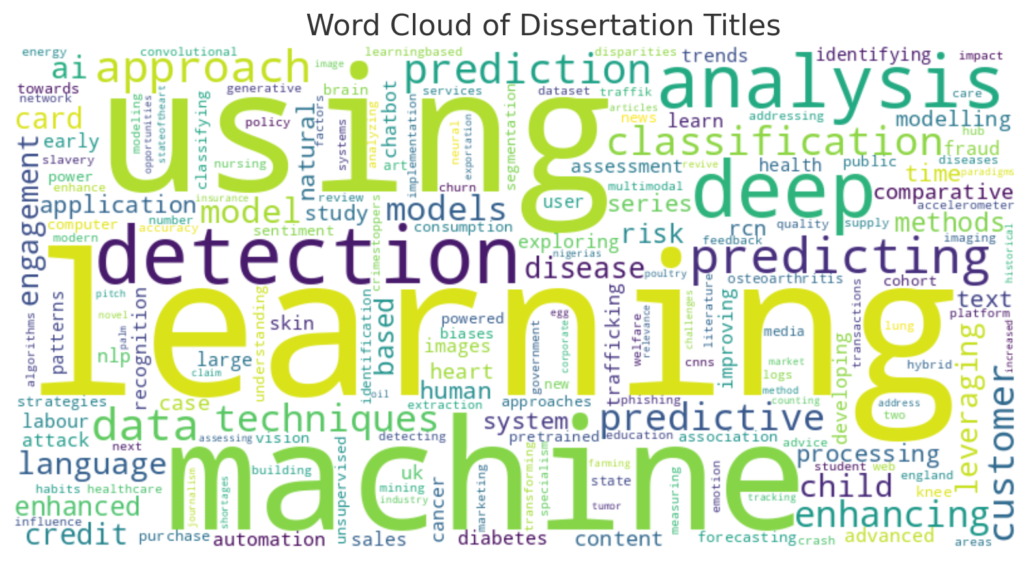
The word cloud visualization above represents the most common words in the dissertation titles after removing stopwords. The larger and bolder the word appears, the more frequently it occurs in the titles.
Topic Modeling Results
Here are the top words in each topic extracted using Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA):
Topic 1:
data, predicting, analysis, content, language, predictive, processing, rcn, uk, natural
Topic 2:
identifying, analysis, text, public, labour, understanding, cnns, implementation, comparative, child
Topic 3:
approach, learning, machine, time, series, predicting, deep, using, sales, habits
Topic 4:
detection, using, learning, machine, card, credit, model, deep, customer, phishing
Topic 5:
learning, using, deep, prediction, models, machine, techniques, detection, analysis, case
Interpretation
The extracted topics suggest the following main themes in the dissertation titles:
Topic 1: Focuses on data analysis, predictive models, and natural language processing.
Topic 2: Involves identifying and analyzing public texts, with applications in labor and child studies.
Topic 3: Centers around machine learning approaches, particularly for time series prediction and sales analysis.
Topic 4: Deals with detection techniques, especially in the context of credit card fraud and phishing using machine learning.
Topic 5: Emphasizes deep learning and machine learning techniques for prediction and detection tasks.
These topics provide insights into the prevalent research areas among the dissertations, highlighting a strong emphasis on machine learning, predictive analytics, and various data analysis techniques.
The data reveals key topics driving academic inquiry within the MSc Data Science and MSc Artificial Intelligence programs. This exploration provides insights into the innovative research contributions of fellow students and the cutting-edge research emerging from the University of Salford. Whether a fellow researcher, a prospective student, or someone curious about current academic trends, this analysis offers a glimpse into the forefront of data science and artificial intelligence research.